Papillomavirus infection is common worldwide. HPV infection occurs regardless of age and sex, but the course of the disease and its development have their own characteristics in men and women.
For the stronger sex, the papilloma virus can cause certain disorders in sexual life and can lead to the development of health problems.
Reasons
Human papillomavirus has such a microscopic structure that it can enter the body through the smallest micro cracks in the skin and mucous membranes.
In this regard, there are several possible HPV infections, including:
- Sexual transmission. Infection can be transmitted not only through simple intimate intercourse, but also through oral contact. In homosexual men, HPV enters through anal contact through cracks in the skin and anus. Trauma to the mucous membrane during intercourse increases the risk of infection.
- The way of life infection. The virus can survive in moist environments for a long time, so it is more likely to be transmitted in bathrooms, saunas, and personal towels. Cases of infection are described in beauty salons, where the rules of disinfection of manicure sets and other tools are ignored. The virus can be transmitted through instruments in dental or surgical rooms.
- From mother to child during childbirth.
Men who change sexual partners frequently become HPV-positive.
It is believed that the younger the girl, the more likely she is to have papillomavirus in her body - most of the detected cases of infection are under the age of 25. Girls can also be infected with HPV because oral and other forms of intercourse are often performed before traditional sex.
Unfortunately, barrier contraception, that is, condoms, cannot guarantee 100% prevention of HPV infection. This is due to the fact that the microorganism, due to its minimal size, easily passes through the pores of the latex. Of course, condoms reduce the chance of infection, but they don't eliminate it completely.
It should also be remembered that the microorganism is present in saliva in a certain amount, so it can also be transmitted through kissing.
Men with bad habits are more likely to get HPV. The probability of infection increases with the weakening of the body's defenses when taking antibiotics and after long-term treatment.
Symptoms
A person may not suspect that he is a carrier of the papillomavirus until he activates the life activity of this microorganism. The reason for this change is often the deterioration of the functioning of the immune defense.
The latent spread of infection lasts from two weeks to a year, and in some cases this interval is much longer.
The activation of the virus causes a part of it to accumulate in a certain place of the skin or mucous membrane. Accumulation and development of the papillomavirus alters the functions of epithelial cells and causes a tumor-like process.
Papillomas can appear almost anywhere on our body, most often they appear on the armpits, face, neck, and genitals. Sometimes the process of formation of papillomas is accompanied by itching and burning.
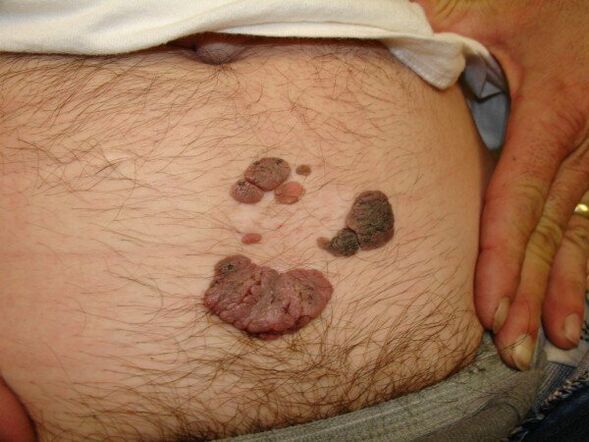
Papillomavirus structures in the body grow in the form of plaques, warts, and filiform bumps on the legs. The most dangerous are genital warts, in men they can grow on the penis, around the anus or inside the urethra.
At first, these growths often look like small pimples, and in advanced cases, they can coalesce and form growths similar to cauliflower in shape.
Genital warts in themselves are unpleasant only because of a cosmetic defect. But if they are not removed and the papillomatous infection is not treated in general, there is a risk that the changed epithelial cells will turn into cancer cells.
Sometimes papillomas are damaged during intercourse or careless movement, causing some bleeding and pain. With the strengthening of the immune system, self-healing often occurs, that is, the papillomas disappear or shrink.
Effects
The consequences of infection with papillomavirus are very unpleasant for men and it depends on the strain of the microorganism.
If the inner part of the urethra is damaged, there is a risk of rapid growth and spread of genital warts inside the urethra. This leads to its partial or complete obstruction, which negatively affects the flow of urine and affects the development of disorders in the functioning of the urinary organs.
The appearance of the growth of worms in the penis, around the anus and the anus increases the likelihood of a malignant structure.
Rectal cancer is most often diagnosed in men who engage in non-traditional sex. When engaging in oral sex, there is a risk of developing papillomas of the throat, which is manifested by various discomforts.
A person infected with HPV also poses a certain risk to the women in his circle. Such a man becomes a source of infection for his wife or other sexual partner. There is a risk of infection when using a towel, bath accessories in the family and sisters, mothers, daughters.
Diagnostic methods

Diagnosis begins with an examination of the external genitalia and the patient's entire body.
The doctor must collect the anamnesis, that is, to clarify when the structure appeared in the body, what the patient associates with their growth, and to determine whether there are certain complaints.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient must undergo several tests, including:
- Swab or scrape from the lining of the urethra.
- PCR test to determine the type of virus, its quantitative content. This test is performed after a smear, prostate secretion, or blood sample.
- Biopsy - examination of a sample of tissue taken during the removal of a genital wart or from a change in the mucous membrane.
- Ureteroscopy helps to visually examine changes in the urethra.
For men who are sexually active, it is recommended that swabs taken from the anal area be tested.
Methods of treatment of papillomavirus in men
Treatment options for human papillomavirus in men depend on which strain of the virus is found in the man.
If a pathogen with high oncogenic activity is detected, then effective antiviral treatment is prescribed, and it is necessary to regularly repeat the tests in the future.
Papillomas and condylomas are removed from the skin and mucous membrane in several ways. It can be conventional scalpel cutting or modern methods - laser treatment, electrocoagulation, radio wave method.
After removing the papilloma, it is necessary to increase the body's resistance to infections, which reduces the risk of transmission of another type of HPV.
Prevention
Prevention of human papillomavirus infection is to be discreet about sex and, if possible, have sex only with trusted partners. Prevention methods include following basic rules in everyday life, such as using your own towels and underwear while maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Infection can be prevented by vaccination. A special vaccine against HPV has been developed, which is given three times at certain intervals. Vaccination leads to the formation of immunity in the body against some strains of papillomavirus.














































































